What is Carpal Tunnel Syndrome and How Can Physical Therapy Help?
What is Carpal Tunnel Syndrome and How Can Physical Therapy Help?
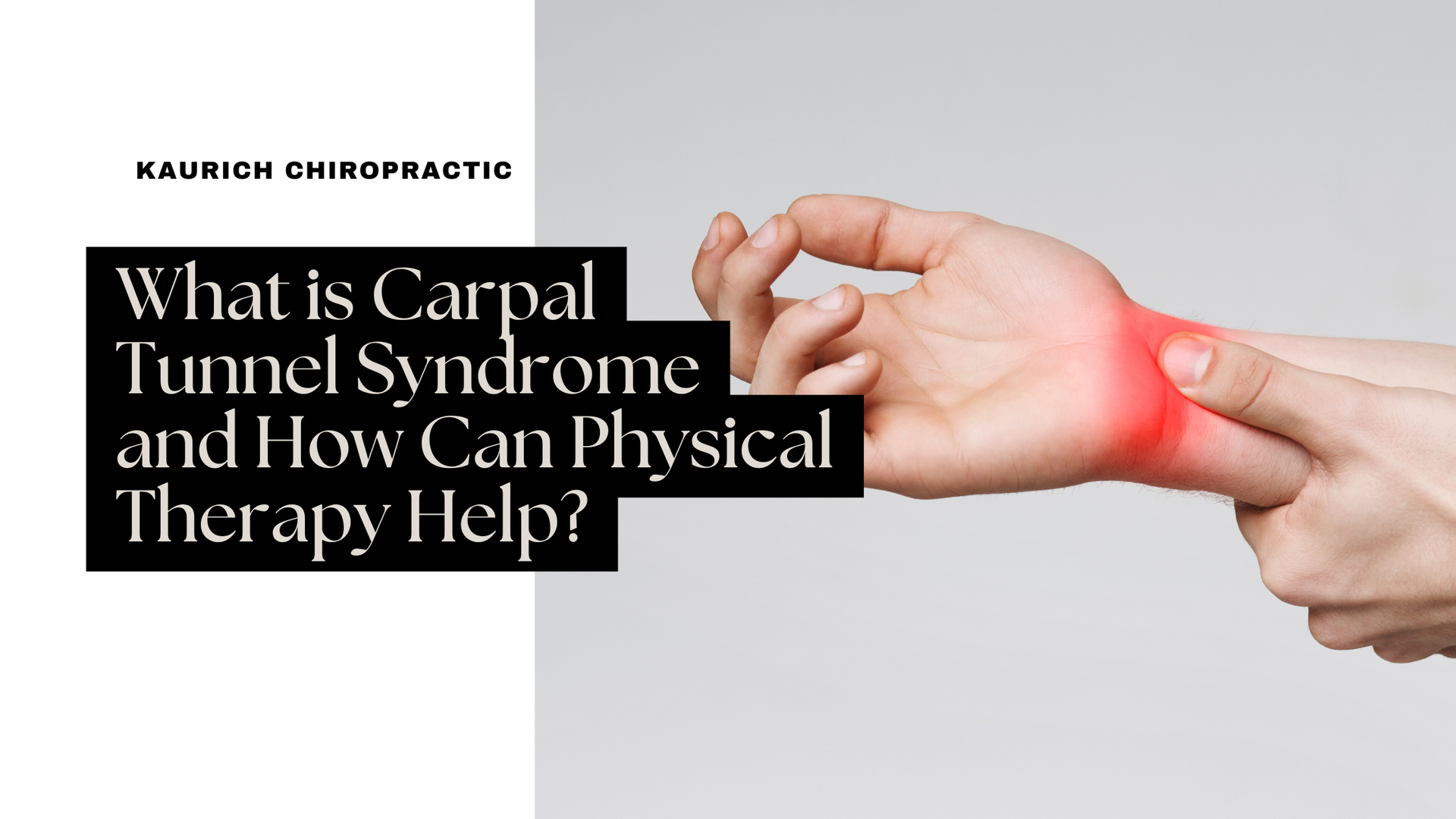
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS) is one of the most common conditions that affects the hands and wrists, causing discomfort and pain, particularly in people who engage in repetitive hand movements. Whether you're a desk worker, a factory worker, or an athlete, the risk of developing this condition can increase due to prolonged strain on the wrists. Fortunately, physical therapy can play a key role in alleviating the symptoms and helping you recover. But before we dive into how physical therapy helps, let’s first understand what Carpal Tunnel Syndrome is.
Understanding Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome occurs when the median nerve, which runs from your forearm into the palm of your hand, becomes compressed as it passes through the carpal tunnel – a narrow passageway in your wrist. This nerve is responsible for controlling sensations in the thumb, index, middle, and part of the ring finger, as well as controlling the muscles at the base of your thumb.
When the carpal tunnel narrows or the tissues surrounding the median nerve become swollen, pressure is placed on the nerve, leading to a range of symptoms that can affect your daily activities.
Common Symptoms of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
- Pain: Often in the wrist, palm, or forearm, particularly during activities that involve repetitive hand or wrist motions.
- Numbness or Tingling: A "pins and needles" sensation in the thumb, index, and middle fingers, which may worsen at night.
- Weakness: Difficulty gripping objects or performing fine motor tasks due to weakened hand muscles.
- Decreased Coordination: Difficulty with precision tasks like typing or buttoning a shirt.
Causes of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
CTS is often caused by repetitive motions and overuse of the wrist. It can also result from:
- Prolonged typing or use of a computer mouse
- Jobs that require frequent use of vibrating tools or repetitive hand movements
- Medical conditions like diabetes, arthritis, or hypothyroidism
- Pregnancy (due to fluid retention)
- Previous wrist injuries
How Can Physical Therapy Help with Carpal Tunnel Syndrome?
Physical therapy is a conservative treatment that aims to reduce symptoms, restore function, and prevent the condition from worsening. It can be highly effective in treating Carpal Tunnel Syndrome, particularly when the condition is diagnosed early or when surgery isn’t necessary. Here's how physical therapy can help:
1. Relieving Pain and Inflammation
Physical therapy can use several techniques to help reduce the inflammation in the wrist and relieve pressure on the median nerve:
- Ice and Heat Therapy: Alternating ice and heat packs can help control swelling, improve circulation, and reduce pain in the wrist.
- Ultrasound Therapy: This technique uses sound waves to penetrate deep into the tissues, promoting healing and reducing inflammation around the nerve.
2. Stretching and Strengthening Exercises
One of the most effective ways to combat Carpal Tunnel Syndrome is through targeted exercises. A physical therapist will guide you through stretches and strengthening exercises that can:
- Stretch the Flexor Muscles: Stretching the muscles and tendons in the forearm and wrist helps reduce tension and inflammation in the carpal tunnel.
- Strengthen the Wrist and Hand Muscles: Strengthening the muscles around the wrist improves support and reduces the stress placed on the median nerve.
For example, exercises such as wrist flexor stretches and nerve gliding exercises (nerve mobilization) help the median nerve glide smoothly through the carpal tunnel, reducing irritation.
3. Posture and Ergonomics Training
Poor posture or improper ergonomics at work can exacerbate Carpal Tunnel Syndrome. A physical therapist will assess your workstation setup and advise on modifications to reduce strain on your wrists and hands. This may include:
- Adjusting the height of your desk or computer monitor
- Recommending wrist supports or ergonomic keyboards
- Educating you on proper wrist positioning during repetitive tasks (e.g., avoiding excessive bending of the wrist while typing or using a mouse)
4. Manual Therapy
Manual therapy involves hands-on techniques to reduce tension in the muscles and joints of the wrist, arm, and neck. Physical therapists may perform gentle mobilizations or massage to release tightness around the wrist joint and improve circulation.
5. Splinting and Bracing
Wearing a wrist splint or brace, especially at night, can help keep your wrist in a neutral position and prevent further compression of the median nerve. Physical therapists often recommend these devices to alleviate symptoms, particularly if you're experiencing numbness and tingling at night.
6. Education and Lifestyle Modifications
In addition to exercises and hands-on treatments, physical therapists provide valuable education on preventing the recurrence of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome. They may:
- Teach you how to take breaks during repetitive tasks
- Suggest stretching routines to incorporate into your daily life
- Provide recommendations for lifestyle changes (such as weight management or dietary adjustments) if underlying medical conditions are contributing to your symptoms.
When to Seek Physical Therapy for Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
If you start experiencing any of the symptoms of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome, it’s important to act early. The earlier you seek treatment, the more effective physical therapy will be in preventing the condition from progressing to the point where surgery may be required. If you have already been diagnosed with CTS or suspect that you may have it, visiting a physical therapist is an excellent first step.
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome doesn’t have to be a life-altering condition. While it can be painful and disruptive, physical therapy offers a range of treatments that can alleviate symptoms, reduce inflammation, and restore function to your hands and wrists. By addressing the root causes and providing targeted exercises and manual therapies, physical therapists can help you manage and even reverse Carpal Tunnel Syndrome without resorting to invasive procedures.
If you’re struggling with the symptoms of CTS, don’t wait for the condition to worsen. Consult with a physical therapist today and take the first step toward regaining pain-free function in your hands and wrists!
GIVE US A CALL TODAY: 574-282-2828
Call Us
Phone support is open from 9 to 5.
Feel free to give us a call.
574-282-2828
Email Us
For general inquiries & questions,
contact us via email
kevin@drkaurich.com
Visit Us
21421 Cleveland Rd
South Bend, IN 46628
View on Map

If you're dealing with pain, stiffness, or just want to feel better in your body, you’ve likely come across a few options: chiropractors, physical therapists, and massage therapists. While each of these professionals focuses on improving your physical health and mobility, they do so in different ways. So how do you know which one is right for you? Let’s break it down. Chiropractors: Spinal Health & Nervous System Function What they do: Chiropractors focus on the alignment of the spine and how it affects your overall health. They use gentle spinal adjustments to correct misalignments (called subluxations) that may be interfering with the nervous system. Common reasons to see a chiropractor: Back and neck pain Headaches or migraines Sciatica Postural issues Preventive wellness care Key approach: Chiropractic care is rooted in the idea that a healthy spine = a healthy body. By restoring proper alignment, chiropractors help your body heal itself naturally. Physical Therapists (PTs): Rehabilitation & Functional Movement What they do: Physical therapists specialize in helping people recover from injuries, surgeries, or physical limitations. Their goal is to restore movement, improve strength, and prevent future injuries through personalized exercises and stretches. Common reasons to see a PT: Recovery from surgery or injury Sports rehab Chronic pain management Improving mobility after a stroke or illness Key approach: PTs design custom rehab programs tailored to your body and goals. Sessions often include exercises, hands-on therapy, and education to improve strength, balance, and mobility. Massage Therapists: Muscle Relaxation & Tension Relief What they do: Massage therapists work on the soft tissues of the body, including muscles, tendons, and ligaments. They use different techniques to relieve tension, promote circulation, and reduce stress. Common reasons to get a massage: Muscle tightness or knots Stress relief Improving circulation Recovery from workouts Supporting relaxation Key approach: Massage is hands-on and therapeutic. Whether it’s deep tissue, Swedish, or trigger point therapy, the focus is on relaxation and muscle relief. So, Which One Should You See? It depends on your needs — and in many cases, a combination of all three offers the best results. Here’s a quick guide: Your Goal Best Fit Spinal alignment, posture, nerve health Chiropractor Recovery from injury or surgery Physical Therapist Relaxation, muscle tension relief Massage Therapist Chronic pain and movement issues Combo: Chiropractor + PT Stress-related tension and tightness Massage Therapist (with chiro care too!) Final Thoughts At the end of the day, your wellness journey is unique. Chiropractors, physical therapists, and massage therapists all bring different tools to the table — and often, they work best together. If you’re not sure where to start, we’re here to help guide you based on your symptoms and goals. Got questions? We’re just a call away. Let’s work together to get you feeling your best.

1 (15 oz) can black beans, drained and rinsed 1/2 cup corn 1/2 bell pepper, chopped 1/2 onion, chopped 1/4 cup cilantro, chopped 1 tablespoon butter or oil 1/2 teaspoon each: paprika, garlic powder, onion powder, cumin, salt, black pepper Juice of 1 lime 1 1/2 cups shredded mozzarella or Mexican blend cheese 2 cups cooked rice (optional) 8 medium flour tortillas Oil or cooking spray, for pan

As the weather warms up and outdoor activities become more frequent, it’s essential to prioritize two key factors for overall well-being: hydration and posture. Whether you're hiking, biking, running, or simply enjoying time outside, these elements play a crucial role in maintaining energy, preventing injuries, and keeping your body functioning at its best. Why Hydration Matters Water is vital for nearly every bodily function, and staying properly hydrated is especially important when engaging in outdoor activities. Here’s why: ✅ Regulates Body Temperature – Sweating helps cool the body, but without enough water, you risk overheating and dehydration. ✅ Prevents Muscle Cramps – Dehydration can lead to muscle fatigue and cramping, reducing performance and increasing injury risk. ✅ Boosts Energy & Focus – Even mild dehydration can cause fatigue, dizziness, and difficulty concentrating. ✅ Supports Joint & Spine Health – Water helps lubricate joints and maintain spinal disc hydration, reducing stiffness and discomfort. 💡 Tip: Carry a reusable water bottle and sip regularly, especially in hot or humid conditions. Electrolyte-rich drinks can be helpful after prolonged activity. The Role of Posture in Outdoor Activities Proper posture is just as important as hydration, helping to prevent injuries and ensuring your body moves efficiently. Here’s how posture affects different activities: 🏃♂️ Running & Walking – Maintain an upright posture with shoulders relaxed and core engaged to avoid back and neck strain. 🚴 Cycling – Keep your back straight and adjust your bike seat to prevent hunching over, which can cause lower back pain. 🥾 Hiking – Use your legs for stability, keep your spine aligned, and avoid slouching, especially when carrying a backpack. 🌿 Gardening & Yard Work – Bend at the knees, not the waist, to protect your lower back from strain. 💡 Tip: Stretch before and after activity to maintain flexibility and prevent stiffness. Regular chiropractic care can also help with alignment and posture correction. Stay Hydrated, Stay Aligned, Stay Active! By prioritizing hydration and proper posture, you can make the most of your outdoor adventures while reducing discomfort and injury risk. If you're experiencing joint pain, muscle tension, or posture-related issues, chiropractic care can help keep your body in top shape. Stand tall, drink up, and enjoy the great outdoors!

Sleep Awareness Week is the perfect time to focus on something we all need but often struggle to get—quality sleep. If you find yourself tossing and turning at night, waking up with aches and pains, or feeling groggy in the morning, your spine and nervous system might be playing a bigger role than you think. The Connection Between Chiropractic Care and Sleep Your spine and nervous system control how your body functions, including your ability to relax and recharge at night. Misalignments in the spine (subluxations) can create tension, discomfort, and nervous system imbalances that interfere with restful sleep. That’s where chiropractic care can help. 1. Reducing Pain for Deeper Sleep Chronic pain—especially in the neck, back, and joints—can make it hard to get comfortable at night. Chiropractic adjustments help relieve tension, reduce inflammation, and promote better spinal alignment, allowing your body to relax more easily. 2. Managing Stress and Promoting Relaxation Your nervous system plays a major role in stress management. When the spine is out of alignment, it can contribute to increased stress, making it harder to unwind. Chiropractic care helps regulate the nervous system, reducing cortisol (the stress hormone) and promoting a sense of calm—essential for quality sleep. 3. Supporting Better Breathing and Sleep Apnea Relief Misalignments in the spine can affect the muscles and nerves responsible for breathing. Chiropractic adjustments may improve airway function and help reduce sleep apnea symptoms, making breathing easier during sleep. 4. Improving Sleep for All Ages Studies have shown that chiropractic care can benefit not just adults, but also children who struggle with sleep disturbances, colic, or restlessness. Proper spinal alignment allows their growing bodies to function optimally, leading to more restful nights. Simple Tips for Better Sleep Along with chiropractic care, here are some tips to improve your sleep quality: ✅ Maintain a Consistent Sleep Schedule – Go to bed and wake up at the same time every day. ✅ Create a Relaxing Bedtime Routine – Avoid screens, caffeine, and heavy meals before bed. ✅ Check Your Pillow and Mattress – A supportive mattress and pillow that align with your spine can make a big difference. ✅ Stretch Before Bed – Gentle stretching or yoga can relieve tension and relax your body for sleep. ✅ Get Regular Adjustments – Chiropractic care keeps your spine aligned and your nervous system balanced for optimal rest. Ready to Sleep Better? We Can Help! If you’re struggling with poor sleep, pain, or stress, chiropractic care may be the missing piece to your wellness routine. During Sleep Awareness Week, make a commitment to your health by prioritizing better rest. Contact us today to schedule an appointment and take the first step toward better sleep and better health! 📞 Call us at 574-282-2828 📍 Visit us at 21421 Cleveland South Bend, Indiana 46628 🌐 Book Online: https://www.kaurichchiropractic.com/

Why People Experience More Activity-Related Injuries in Spring As the weather warms up and daylight hours increase, many people feel motivated to get outside and be more active. Whether it's jogging, hiking, gardening, or playing sports, spring invites a surge in physical activity. However, this seasonal shift also comes with an increased risk of injuries. Understanding why injuries are more common in the spring can help you take steps to prevent them and stay active safely. 1. Sudden Increase in Activity Levels During the winter months, many people adopt a more sedentary lifestyle. When spring arrives, they often jump into physical activities without properly preparing their bodies. This sudden increase in movement can lead to muscle strains, joint pain, and even more serious injuries like sprains or fractures. 2. Deconditioned Muscles and Joints A lack of regular movement during winter can cause muscles to weaken and joints to become less flexible. Without proper conditioning, the body is more susceptible to injuries when engaging in high-impact or repetitive activities such as running or cycling. 3. Increased Outdoor Sports Participation Spring is a popular time for sports like baseball, soccer, and tennis. These sports involve quick movements, sudden stops, and twisting motions that can put stress on the muscles and joints. Without proper warm-ups and stretching, athletes are at a higher risk of sprains, ligament tears, and overuse injuries. 4. Uneven Terrain and Unpredictable Weather Outdoor environments can pose additional risks. Trails, parks, and fields may have uneven surfaces, leading to ankle sprains or falls. Additionally, unpredictable spring weather, including rain and wet conditions, can make outdoor surfaces slippery, increasing the chances of injury. 5. Overexertion and Enthusiasm The excitement of warmer weather can sometimes lead people to push themselves too hard, too soon. Overexertion without proper pacing or rest can cause fatigue-related injuries, including muscle cramps, stress fractures, and tendonitis. How to Prevent Spring Activity Injuries Gradually increase activity levels to allow your body to adjust. Stretch and warm up properly before engaging in physical activity. Strengthen muscles and improve flexibility with targeted exercises. Stay hydrated and listen to your body to avoid overexertion. Use proper gear and footwear to support your joints and prevent falls. Consider chiropractic care to keep your body aligned and functioning optimally. Spring is a wonderful time to get moving, but staying mindful of these risks can help ensure a pain-free and enjoyable season. By taking preventative measures, you can make the most of your favorite spring activities without injury!

Directions Prepare the Salmon: Start by patting the salmon fillet dry with a paper towel. Remove the skin if preferred and cut the fillet into bite-sized cubes. Heat the Pan: Heat olive oil in a large skillet over medium heat. Once hot, add the salmon bites, placing them in a single layer. Sear the pieces for 2-3 minutes on each side until they are golden brown and cooked through. Remove the salmon from the skillet and set aside. Make the Sauce: In the same skillet, lower the heat slightly and add minced garlic. Sauté for about 30 seconds until fragrant. Stir in honey, soy sauce, and lemon juice. Let the mixture simmer for 2-3 minutes until it thickens slightly. Thicken the Glaze: In a small bowl, whisk cornstarch with water to create a slurry. Slowly add this to the simmering sauce, stirring constantly to ensure no lumps form. Cook for another minute or two until the glaze reaches a rich, glossy consistency. Coat the Salmon: Return the salmon bites to the skillet and gently toss them in the honey garlic glaze until fully coated. Let them warm through for about 1-2 minutes. Serve: Transfer the salmon bites to a serving plate, garnish with chopped fresh parsley if desired, and enjoy immediately.

When you’re looking to increase the protein in your diet, plan each meal with a protein source in mind. If you’re aiming to eat more protein without overdoing it or losing sight of other nutritional needs, one of the easiest ways is to start tracking your food. Meat, Poultry, and Game Bacon, turkey (2 slices / 16 g): 5 g of protein Beef, cooked (3 oz / 85 g): 21 g of protein Bison, cooked and ground (3 oz / 85 g): 22 g of protein Chicken breast, cooked (3 oz / 85 g): 26 g of protein Chicken thighs, cooked (3 oz / 85 g): 21 g of protein Duck, cooked (3 oz / 85 g): 20 g of protein Ground turkey, cooked (3 oz / 85 g): 23 g of protein Italian sausage, cooked (1 link / 75 g): 14 g of protein Lamb, cooked (3 oz / 85 g): 21 g of protein Pork, cooked (3 oz / 85 g): 22 g of protein Pork chops, cooked (3 oz / 85 g): 23 g of protein Quail, cooked (3 oz / 85 g): 21 g of protein Rabbit, cooked (3 oz / 85 g): 27 g of protein Turkey breast, cooked (3 oz / 85 g): 26 g of protein Veal, cooked (3 oz / 85 g): 22 g of protein Venison, cooked (3 oz / 85 g): 24 g of protein Dairy & Eggs Cheddar cheese (1 oz / 28 g): 7 g of protein Cottage cheese (1/2 cup / 112 g): 13 g of protein Eggs, whole (1 large): 6 g of protein Feta cheese (1 oz / 28 g): 4 g of protein Greek yogurt, plain (6 oz / 170 g): 17 g of protein Ice cream, vanilla (1 cup / 135 g): 5 g of protein Kefir (1 cup / 240 mL): 8-11 g of protein Milk (1 cup / 240 mL): 8 g of protein Mozzarella cheese (1 oz / 28 g): 7 g of protein Parmesan cheese (1 oz / 28 g): 10 g of protein Ricotta cheese (1/2 cup / 124 g): 12 g of protein Swiss cheese (1 oz / 28 g): 8 g of protein Yogurt, plain (1 cup / 245 g): 13 g of protein Nuts and Seeds Almonds (1 oz / 28 g): 6 g of protein Chia seeds (2 tbsp / 28 g): 5 g of protein Flaxseeds (2 tbsp / 14 g): 3 g of protein Hemp seeds (3 tbsp / 30 g): 9 g of protein Nuts (mixed, 1 oz / 28 g): 5 g of protein Pistachios (1 oz / 28 g): 6 g of protein Pumpkin seeds (1 oz / 28 g): 8 g of protein Sunflower seeds (1 oz / 28 g): 6 g of protein Walnuts (1 oz / 28 g): 4 g of protein Grains and Pseudograins Amaranth, cooked (1 cup / 246 g): 9 g of protein Buckwheat, cooked (1 cup / 168 g): 6 g of protein Bulgur wheat, cooked (1 cup / 182 g): 6 g of protein Farro, cooked (1 cup / 195 g): 12 g of protein Nutritional yeast (1 tbsp / 5 g): 2.5 g of protein Oats, cooked (1 cup / 240 g): 5 g of protein Quinoa, cooked (1 cup / 170 g): 8 g of protein Teff, cooked (1 cup / 252 g): 10 g of protein Udon noodles, cooked (1 cup / 180 g): 7 g of protein Ziti pasta, cooked (1 cup / 140 g): 8 g of protein Vegetables Asparagus, cooked (1 cup / 180 g): 4 g of protein Black-eyed peas, cooked (1/2 cup / 93 g): 7 g of protein 93g /7g protein Broccoli, cooked (1 cup / 156 g): 4 g of protein Eggplant, cooked (1 cup /95 g): 1 g of protein Green peas, cooked (1 cup / 160 g): 9 g of protein Jicama (1 cup / 130 g): 1 g of protein Kale, cooked (1 cup / 130 g): 4 g of protein Mushroom, white (1 cup/155g0g 5.6 g of protein Peas, cooked (1/2 cup /80 g): 4 g of protein Spinach, cooked (1 cup / 180 g): 6 g of protein Watercress, raw (1 cup / 34 g): 1 g of protein Zucchini, cooked (1 cup / 180 g): 2 g of protein Legumes Black beans, cooked (1/2 cup / 90 g): 8 g of protein Chickpeas, cooked (1/2 cup / 90 g): 8 g of protein Edamame, cooked (1/2 cup / 78 g): 8 g of protein Garbanzo beans (1/2 cup / 90 g): 8 g of protein Kidney beans, cooked (1/2 cup / 90 g): 7 g of protein Lentils, cooked (1/2 cup / 90 g): 9 g of protein Lima beans, cooked (1/2 cup / 90 g): 5 g of protein Red lentils, cooked (1/2 cup / 90 g): 9 g of protein Fruits Avocado, one fruit (150 g): 3 g of protein Banana, one fruit (126 g): 1 g of protein Dates, dried (1/4 cup / 40 g): 1 g of protein Jackfruit (1 cup / 178 g): 4 g of protein

A healthy diet can play a significant role in supporting spinal health by providing essential nutrients that strengthen bones, maintain spinal discs, and reduce inflammation. Here are some foods and nutrients to include: 1. Calcium-Rich Foods Calcium is crucial for maintaining strong bones, including the vertebrae in your spine. Examples: Dairy products (milk, yogurt, cheese), leafy greens (kale, spinach, collard greens), almonds, fortified plant-based milk. 2. Vitamin D Vitamin D helps your body absorb calcium effectively. Examples: Fatty fish (salmon, mackerel), egg yolks, fortified foods, or safe sun exposure for natural vitamin D production. 3. Omega-3 Fatty Acids Omega-3s have anti-inflammatory properties, which can help reduce back pain caused by inflammation. Examples: Fatty fish (salmon, sardines), walnuts, flaxseeds, chia seeds. 4. Magnesium Magnesium supports muscle and nerve function and helps maintain bone density. Examples: Nuts (almonds, cashews), seeds, whole grains, avocados, and bananas. 5. Collagen-Boosting Foods Collagen supports the spinal discs and connective tissues. Examples: Bone broth, citrus fruits (for vitamin C to aid collagen production), berries, and fish. 6. Anti-Inflammatory Foods These foods help combat inflammation, which can contribute to spinal pain and stiffness. Examples: Turmeric, ginger, green tea, leafy greens, and colorful fruits like berries and oranges. 7. Hydrating Foods Spinal discs need water to maintain their cushioning properties. Examples: Water-rich foods like cucumbers, watermelon, oranges, and soups, along with plenty of plain water. 8. Protein-Rich Foods Protein is essential for repairing tissues, including muscles and ligaments around the spine. Examples: Lean meats, fish, eggs, tofu, legumes, and nuts. 9. Foods Rich in Vitamin K Vitamin K supports bone health by helping regulate calcium. Examples: Leafy greens (kale, spinach), broccoli, and Brussels sprouts. 10. Zinc-Rich Foods Zinc aids tissue repair and supports the healing process. Examples: Shellfish, nuts, seeds, and whole grains. Tips for Optimal Spinal Health Maintain a balanced diet with a variety of whole foods. Limit processed foods, sugary snacks, and trans fats that can promote inflammation. Stay hydrated to support overall disc and joint health. Pairing a nutritious diet with regular exercise, good posture, and proper lifting techniques can help keep your spine healthy and strong for years to come! 💪




